Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray analysis
-ray analysis木下 哲一*; 能任 琢真*; 中島 均*; 小迫 和明*; 加藤 雄大*; 黒岩 洋一*; 倉部 美彩子*; 佐々木 勇気*; 鳥居 和敬*; 前田 亮; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(2), p.479 - 486, 2023/02
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:43.92(Chemistry, Analytical)There are some different chemical and physical forms of water molecules in concretes. Especially, bound water is difficult to determine. In the present work, we determined free + adsorbed water and bound water contained in aggregates and cement pastes, which are component of concretes, by means of conventional gravimetric analysis and prompt  -ray analysis (PGA), respectively, in order to evaluate a total water content in concretes. In the PGA, background reduction was attempted by using the time-of-flight (TOF) signal. In addition, the degree of contribution to analytical values by scattered neutrons by samples was evaluated because water would adsorb on the surface of instruments inside the irradiation chamber for the PGA. Contents of the free + adsorbed water and bound water in some geochemical references determined in the present work were compared with the nominal values to confirm the precision. Each water content in aggregates collected from different quarries and cement pastes with different water-to-cement ratios were analyzed. A total water content in young concrete was evaluated on the basis of the analytical values.
-ray analysis (PGA), respectively, in order to evaluate a total water content in concretes. In the PGA, background reduction was attempted by using the time-of-flight (TOF) signal. In addition, the degree of contribution to analytical values by scattered neutrons by samples was evaluated because water would adsorb on the surface of instruments inside the irradiation chamber for the PGA. Contents of the free + adsorbed water and bound water in some geochemical references determined in the present work were compared with the nominal values to confirm the precision. Each water content in aggregates collected from different quarries and cement pastes with different water-to-cement ratios were analyzed. A total water content in young concrete was evaluated on the basis of the analytical values.
藤 暢輔; 大図 章; 土屋 晴文; 古高 和禎; 北谷 文人; 米田 政夫; 前田 亮; 小泉 光生
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2021/08
Since neutrons have exceptional ability to penetrate high-density materials and can induce fission, they are used in non-destructive analysis such as, Differential Die-Away Analysis (DDA), Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA) and Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA). The different analytical methods give us complementary information, which are particularly useful for the quantification of Special Nuclear Materials in highly radioactive nuclear materials, including spent fuel. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission are collaborating to develop an active neutron NDA system for nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security. In the second phase of the project, an integrated active neutron NDA system: Active-N which enables the simultaneous measurements of DDA, PGA and NRTA has been developed. The DDA detects fission neutrons, and it can determine small amounts of the fissile mass. PGA is utilized for the quantification of neutron absorber and particularly useful for the detection of explosives. NRTA can be used to quantify almost all medium and high-Z elements and considered as one of the most accurate NDA. In this presentation, we will provide an overview of Active-N and report the recent experimental results. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion of MEXT: Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
古高 和禎; 大図 章; 藤 暢輔
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/08
We have been developing an integrated active neutron non-destructive analysis system for highly radioactive nuclear materials, "Active-N", using an intense D-T neutron source. The system is composed of the following mutually complementing different measurement systems: Differential Die-away Analysis (DDA), Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA), and Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA). The former two are for measurements of total amount of fissile material and of isotopic composition, respectively. The purpose of the last one, i.e. PGA measurement system is the detection of explosives contained in e.g., dirty bombs and of chemical warfare agents, as well as of neutron poisons which absorb neutrons and disturb DDA measurements. This report describes mainly the PGA measurement system. In the PGA measurement system, to resolve individual gamma-ray peaks, a Ge detector is utilized. It is well known that irradiation of fast neutrons (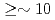 keV) to Ge detectors cause damages to the detectors and gradually worsen their resolution, and finally make them unusable without a laborious treatment. Therefore, it is essential to shield the PGA detector against the neutrons from the D-T neutron generator. In addition, to reduce background gamma rays from the materials used for the DDA system, they should also be carefully chosen. In order to design an appropriate neutron shield for the PGA measurement system and diminish the sources of the background gamma rays, simulation study was done using a particle transport code system PHITS. Based on the results, a shielding for the PGA measurement system has been designed which reduces the number of damaging neutrons by an order of magnitude. The Active-N system which incorporates the PGA measurement system equipped with the neutron shielding, has been installed at NUCEF facility in JAEA Tokai. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion from MEXT.
keV) to Ge detectors cause damages to the detectors and gradually worsen their resolution, and finally make them unusable without a laborious treatment. Therefore, it is essential to shield the PGA detector against the neutrons from the D-T neutron generator. In addition, to reduce background gamma rays from the materials used for the DDA system, they should also be carefully chosen. In order to design an appropriate neutron shield for the PGA measurement system and diminish the sources of the background gamma rays, simulation study was done using a particle transport code system PHITS. Based on the results, a shielding for the PGA measurement system has been designed which reduces the number of damaging neutrons by an order of magnitude. The Active-N system which incorporates the PGA measurement system equipped with the neutron shielding, has been installed at NUCEF facility in JAEA Tokai. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion from MEXT.
 Pd and
Pd and  Tc
Tc藤 暢輔; 瀬川 麻里子; 前田 亮; 常山 正幸*; 木村 敦; 中村 詔司; 遠藤 駿典; 海老原 充*
Analytical Chemistry, 93(28), p.9771 - 9777, 2021/07
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:37.70(Chemistry, Analytical)Considering the expanding demand for nuclear waste management of the spent nuclear fuel materials in near future, a non-destructive analytical scheme applicable to the most difficult-to-measure nuclide of  Pd, which emits no decay gamma-rays and whose half-life is too long to be decayed out during a human lifetime, was designed. The scheme consists of a sophisticated instrument capable of the detection of gamma-rays by Ge detectors coupled with time-of-flight measurement of neutrons and a high-intensity pulsed neutron beam, and can simultaneously perform TOF-coupled prompt gamma-ray analysis (TOF-PGA) as well as PGA and NRCA. An analytical capability was evaluated by applying to simulated samples of the Tc-platinum group metals (Tc-PGMs) obtained by the group partitioning process of spent nuclear fuels, which contain not only
Pd, which emits no decay gamma-rays and whose half-life is too long to be decayed out during a human lifetime, was designed. The scheme consists of a sophisticated instrument capable of the detection of gamma-rays by Ge detectors coupled with time-of-flight measurement of neutrons and a high-intensity pulsed neutron beam, and can simultaneously perform TOF-coupled prompt gamma-ray analysis (TOF-PGA) as well as PGA and NRCA. An analytical capability was evaluated by applying to simulated samples of the Tc-platinum group metals (Tc-PGMs) obtained by the group partitioning process of spent nuclear fuels, which contain not only  Pd but also
Pd but also  Tc and another difficult-to-measure fission product. It was confirmed that, although PGA and NRCA could accurately analyze both nuclides in individual single substances, only TOF-PGA can analyze
Tc and another difficult-to-measure fission product. It was confirmed that, although PGA and NRCA could accurately analyze both nuclides in individual single substances, only TOF-PGA can analyze  Pd as well as
Pd as well as  Tc in the Tc-PGMs simulated sample. The TOF-PGA measurement technique can be widely used for the non-destructive analysis of
Tc in the Tc-PGMs simulated sample. The TOF-PGA measurement technique can be widely used for the non-destructive analysis of  Pd and
Pd and  Tc in nuclear wastes.
Tc in nuclear wastes.
土屋 晴文; 榎戸 輝揚*; 和田 有希*; 古田 禄大; 中澤 知洋*; 湯浅 孝行*; 楳本 大悟*; 牧島 一夫*; GROWTH Collaboration*
Proceedings of Science (Internet), 358, p.1163_1 - 1163_6, 2021/07
Since 2006, the GROWTH experiment has been successfully operating at the coastal area of Japan Sea. The GROWTH experiment aims at elucidating how particles in lightning and thunderclouds are accelerated to relativistic energies to produce gamma rays and occasionally neutrons. According to observations done by the GROWTH experiment, it is found that there are two types of radiation bursts associated with winter thunderstorms. One is long bursts lasting for a few tens of seconds to a few minutes, being not clearly related to lightning. The other is short bursts in association with lightning. To better understand the production mechanism of these radiation bursts, we have developed a small-type of radiation detectors and increased observational points with the new detectors. In this presentation, we show an overview of observations done by the GROWTH experiment. Then we focus on recent several findings observed by the new detectors. One, which is categorized into long bursts, implies a relationship between a long burst and an intra/inter-cloud discharge. Another is a combination of short bursts and long ones, showing simultaneous detections of prompt gamma rays extending up to 10 MeV and the 511-keV annihilation ones. These gamma-ray signals demonstrate the occurrence of photonuclear reactions in lightning. Based on these results, we discuss the production mechanism of gamma rays related to thunderstorms.
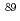 Y
Y片渕 竜也*; 藤 暢輔; 水本 元治*; 齋藤 辰宏*; 寺田 和司*; 木村 敦; 中村 詔司; Huang, M.*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; 井頭 政之*
European Physical Journal A, 57(1), p.4_1 - 4_4, 2021/01
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:43.33(Physics, Nuclear)A new neutron resonance of 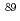 Y was found in time-of-flight (TOF) neutron capture experiments using a pulsed neutron beam from a spallation neutron source of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. The observed resonance energy was 19.7 eV that is much lower than the lowest energy (2.60 keV) of the previous reported resonances. In addition to the TOF measurement, nuclide identification of the resonance was made by prompt
Y was found in time-of-flight (TOF) neutron capture experiments using a pulsed neutron beam from a spallation neutron source of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. The observed resonance energy was 19.7 eV that is much lower than the lowest energy (2.60 keV) of the previous reported resonances. In addition to the TOF measurement, nuclide identification of the resonance was made by prompt  -ray analysis. Neutron capture
-ray analysis. Neutron capture  -rays from
-rays from 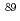 Y were clearly observed only on the resonance. Resonance analysis was applied to the experimental results and the resonance parameters of the new resonance are given.
Y were clearly observed only on the resonance. Resonance analysis was applied to the experimental results and the resonance parameters of the new resonance are given.
 scintillation detector equipped with specially-designed shield for neutron resonance capture analysis
scintillation detector equipped with specially-designed shield for neutron resonance capture analysis土屋 晴文; 小泉 光生; 北谷 文人; 原田 秀郎
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 932, p.16 - 26, 2019/07
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:11.14(Instruments & Instrumentation)A large-volume ( 12.0 cm
12.0 cm 12.7 cm) LaBr
12.7 cm) LaBr scintillation detector equipped with a specially-designed radiation shield was evaluated for neutron resonance capture analysis at the neutron time-of-flight (TOF) facility GELINA. By using the LaBr
scintillation detector equipped with a specially-designed radiation shield was evaluated for neutron resonance capture analysis at the neutron time-of-flight (TOF) facility GELINA. By using the LaBr detector with and without the shield, measurements were carried out at a 13-m TOF station with three metallic samples, namely, Ni, Cr, and Fe. In addition, Monte Carlo simulations with Geant4 were performed, and the results were compared with the measurements to analyze the observed energy spectra and TOF spectra. Energy spectra obtained with the shield showed that prompt
detector with and without the shield, measurements were carried out at a 13-m TOF station with three metallic samples, namely, Ni, Cr, and Fe. In addition, Monte Carlo simulations with Geant4 were performed, and the results were compared with the measurements to analyze the observed energy spectra and TOF spectra. Energy spectra obtained with the shield showed that prompt  -ray peaks emitted from each sample can be used to identify the isotopes. Moreover, the signal-to-noise ratios of resonance peaks in a TOF spectrum with the shield were enhanced 1.5-2.5 in comparison with those without the shield. Furthermore, simultaneous measurements conducted using the three samples demonstrated that the shield employed herein was indispensable for identifying impurities in a composite sample such as particle-like fuel debris.
-ray peaks emitted from each sample can be used to identify the isotopes. Moreover, the signal-to-noise ratios of resonance peaks in a TOF spectrum with the shield were enhanced 1.5-2.5 in comparison with those without the shield. Furthermore, simultaneous measurements conducted using the three samples demonstrated that the shield employed herein was indispensable for identifying impurities in a composite sample such as particle-like fuel debris.
 -ray analysis
-ray analysisHuang, M.; 藤 暢輔; 海老原 充*; 木村 敦; 中村 詔司
Journal of Applied Physics, 121(10), p.104901_1 - 104901_7, 2017/03
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:13.29(Physics, Applied)A new analytical technique, time-of-flight prompt  -ray analysis, has been developed at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. In order to apply it to accurate elemental analysis, a set of standard Fe and Au samples were measured to examine the factors which affect the number of detected events. It was found that the main contributing factors included the attenuations of neutrons and
-ray analysis, has been developed at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex. In order to apply it to accurate elemental analysis, a set of standard Fe and Au samples were measured to examine the factors which affect the number of detected events. It was found that the main contributing factors included the attenuations of neutrons and  rays in the sample, live-time ratio of the data acquisition system and signal pile-up correction factor. A simulation model was built for the estimations of neutron and
rays in the sample, live-time ratio of the data acquisition system and signal pile-up correction factor. A simulation model was built for the estimations of neutron and  -ray attenuations. A simple empirical formula was proposed to calculate the signal pile-up correction factor. The whole correction method has proven to be accurate and reliable.
-ray attenuations. A simple empirical formula was proposed to calculate the signal pile-up correction factor. The whole correction method has proven to be accurate and reliable.
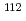 Cd(
Cd( )
) Cd reaction using neutron beams at J-PARC
Cd reaction using neutron beams at J-PARC早川 岳人*; 藤 暢輔; Huang, M.; 静間 俊行*; 木村 敦; 中村 詔司; 原田 秀郎; 岩本 信之; 千葉 敏*; 梶野 敏貴*
Physical Review C, 94(5), p.055803_1 - 055803_6, 2016/11
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:30.95(Physics, Nuclear)The astrophysical origin of a rare isotope  Sn has remained still an open question. An isomer (
Sn has remained still an open question. An isomer (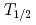 =14.1 y) in
=14.1 y) in  Cd is an s-process branching point from which a nucleosynthesis flow reaches to
Cd is an s-process branching point from which a nucleosynthesis flow reaches to  Sn. The
Sn. The  -process abundance of
-process abundance of  Sn depends on the isomer production ratio in the
Sn depends on the isomer production ratio in the 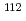 Cd(
Cd( )
) Cd reaction. However, the ratio has not been measured in an energy region higher than the thermal energy. We have measured
Cd reaction. However, the ratio has not been measured in an energy region higher than the thermal energy. We have measured  rays following neutron capture reactions on
rays following neutron capture reactions on 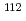 Cd using two cluster HPGe detectors in conjunction with a time-of-flight method at J-PARC. We have obtained the result that the relative
Cd using two cluster HPGe detectors in conjunction with a time-of-flight method at J-PARC. We have obtained the result that the relative  -ray intensity ratio of the isomer is almost constant in an energy region of up to 5 keV. This result suggests that the
-ray intensity ratio of the isomer is almost constant in an energy region of up to 5 keV. This result suggests that the  -process contribution to the solar abundance of
-process contribution to the solar abundance of  Sn is negligibly small. We have found that the ratio of a resonance at 737 eV shows about 1.5 times higher than other ratios. This enhancement can be explained by a
Sn is negligibly small. We have found that the ratio of a resonance at 737 eV shows about 1.5 times higher than other ratios. This enhancement can be explained by a  -wave neutron capture. This result suggests measurements of decay
-wave neutron capture. This result suggests measurements of decay  rays to isomers are effective to assign the spin and parity for neutron capture resonances.
rays to isomers are effective to assign the spin and parity for neutron capture resonances.
 線分析法開発
線分析法開発藤 暢輔; 海老原 充*; Huang, M.; 木村 敦; 中村 詔司; 原田 秀郎
放射化学, (33), p.1 - 9, 2016/03
中性子即発 線分析(PGA)は、中性子捕獲反応に伴って放出される即発
線分析(PGA)は、中性子捕獲反応に伴って放出される即発 線により元素分析を行う方法で、迅速に多元素を非破壊分析できるという特長がある。そのため、宇宙化学・環境・考古学・材料など幅広い分野で用いられ、多くの研究に貢献している。PGAはこれまでに同時計数法や反同時計数法によって検出限界や峻別性能の改良がおこなわれてきたが、大強度陽子加速器施設(J-PARC)の物質・生命科学実験施設(MLF)における大強度パルス中性子ビームによって、飛行時間法を用いた即発
線により元素分析を行う方法で、迅速に多元素を非破壊分析できるという特長がある。そのため、宇宙化学・環境・考古学・材料など幅広い分野で用いられ、多くの研究に貢献している。PGAはこれまでに同時計数法や反同時計数法によって検出限界や峻別性能の改良がおこなわれてきたが、大強度陽子加速器施設(J-PARC)の物質・生命科学実験施設(MLF)における大強度パルス中性子ビームによって、飛行時間法を用いた即発 線分析(TOF-PGA)の利用が可能となった。本稿では同時計数法による即発
線分析(TOF-PGA)の利用が可能となった。本稿では同時計数法による即発 線分析(MPGA)のほか、MLFに設置された中性子核反応測定装置(ANNRI)の概要と本装置によって可能となるTOF-PGAについて解説する。
線分析(MPGA)のほか、MLFに設置された中性子核反応測定装置(ANNRI)の概要と本装置によって可能となるTOF-PGAについて解説する。
藤 暢輔; Huang, M.; 木村 敦; 中村 詔司; 原田 秀郎; 海老原 充*
四季, 28, P. 4, 2015/09
中性子核反応測定装置ANNRIは、高検出効率の即発 線検出装置、高性能なデータ収集系等を備えているほか、広いエネルギーレンジの中性子を用いることができる。中性子を用いた非破壊分析法の一つである即発
線検出装置、高性能なデータ収集系等を備えているほか、広いエネルギーレンジの中性子を用いることができる。中性子を用いた非破壊分析法の一つである即発 線分析(PGA)は、非破壊・多元素同時・バルク分析などの特徴を持つため貴重な試料や破壊が困難な試料の分析に有効である。ANNRIではパルス中性子を用いることができるため、中性子捕獲反応における共鳴を使った分析(中性子共鳴捕獲分析法)も行うことができる。物質・生命科学実験施設MLFから得られる大強度パルス中性子と大立体角を持つゲルマニウム検出器等を用いることによってゲルマニウム検出器でも中性子共鳴捕獲分析を行うことを可能とし、2つの手法を融合した新しい手法を確立した。これによってPGAと中性子共鳴捕獲分析の2つの結果が同時に得られるだけでなく、2つの分析手法の融合による相乗効果が得られる。つまり、PGAでも中性子共鳴捕獲分析でも測定が困難であるものでも分析できるようになった。本論文では、開発した手法について混合標準試料を用いた実験をもとにその特長についての解説を行う。
線分析(PGA)は、非破壊・多元素同時・バルク分析などの特徴を持つため貴重な試料や破壊が困難な試料の分析に有効である。ANNRIではパルス中性子を用いることができるため、中性子捕獲反応における共鳴を使った分析(中性子共鳴捕獲分析法)も行うことができる。物質・生命科学実験施設MLFから得られる大強度パルス中性子と大立体角を持つゲルマニウム検出器等を用いることによってゲルマニウム検出器でも中性子共鳴捕獲分析を行うことを可能とし、2つの手法を融合した新しい手法を確立した。これによってPGAと中性子共鳴捕獲分析の2つの結果が同時に得られるだけでなく、2つの分析手法の融合による相乗効果が得られる。つまり、PGAでも中性子共鳴捕獲分析でも測定が困難であるものでも分析できるようになった。本論文では、開発した手法について混合標準試料を用いた実験をもとにその特長についての解説を行う。
藤 暢輔; 海老原 充*; Huang, M.; 木村 敦; 中村 詔司; 原田 秀郎
Isotope News, (736), p.22 - 26, 2015/08
中性子核反応測定装置(ANNRI)は、J-PARC MLFに設置された即発 線測定実験のための装置であり、主に核データ測定、天体核物理および元素分析の研究開発が行われている。中性子ビームを用いた元素分析法には2つの代表的な手法があり、一つは中性子捕獲
線測定実験のための装置であり、主に核データ測定、天体核物理および元素分析の研究開発が行われている。中性子ビームを用いた元素分析法には2つの代表的な手法があり、一つは中性子捕獲 線のエネルギーを用いる即発
線のエネルギーを用いる即発 線分析(PGA)、もう一つは飛行時間法(TOF)から得られる中性子エネルギーを用いる中性子共鳴捕獲分析である。ANNRIでは大強度パルス中性子ビームと高効率Ge検出器を用いることによって、前述の2つの元素分析法を融合した新しい元素分析法を行うことができる。新しい手法では3次元スペクトル(TOF-PGAスペクトル)を解析することによって従来法では解析が困難な場合でも正確な値が得られることを混合標準試料の測定結果によって示した。今後は非破壊分析が望まれる様々な分野において用いられるものと期待している。
線分析(PGA)、もう一つは飛行時間法(TOF)から得られる中性子エネルギーを用いる中性子共鳴捕獲分析である。ANNRIでは大強度パルス中性子ビームと高効率Ge検出器を用いることによって、前述の2つの元素分析法を融合した新しい元素分析法を行うことができる。新しい手法では3次元スペクトル(TOF-PGAスペクトル)を解析することによって従来法では解析が困難な場合でも正確な値が得られることを混合標準試料の測定結果によって示した。今後は非破壊分析が望まれる様々な分野において用いられるものと期待している。
小林 捷平*
JNC TJ9400 2000-009, 63 Pages, 2000/02
本研究の前半では、長半減期を有する核分裂生成物(FP)の代表的核種であるTc-99について、まず、中性子核データの現状、評価済核データについて調査を行った。次に、京都大学原子炉実験所の電子線型加速器と組み合わせて付設されている京都大学鉛スペクトロメータ(KULS)を用いて、99Tc(n, )100Tc反応断面積を熱中性子から1keVのエネルギー領域において測定した。中性子捕獲によって放出される即発ガンマ線は、アルゴンガス入り比例計数管を用いて測定した。入射中性子束/スペクトルの測定はBF3比例計数管によって行い、捕獲断面積の絶対値は10B(n,
)100Tc反応断面積を熱中性子から1keVのエネルギー領域において測定した。中性子捕獲によって放出される即発ガンマ線は、アルゴンガス入り比例計数管を用いて測定した。入射中性子束/スペクトルの測定はBF3比例計数管によって行い、捕獲断面積の絶対値は10B(n, )反応によって求めた相対測定値をTc-99の熱中性子断面積に規格化した。Tc-99試料に対する中性子自己遮蔽効果は、MCNPコードを用いた計算によって補正した。Chouらが鉛スペクトロメータを用いて測定したTc-99の中性子捕獲断面積は、本測定値より全体に高いがエネルギー依存性はよく一致している。ENDF/B-VI、JENDL-3.2の評価済核データは、5.6、20eV共鳴領域及び数100keV以上で高くなっている。本研究の後半では、鉛スペクトロメータの原理とその構築、諸特性についてまとめた。中でも、KULSの特性として(1)中性子減速時間t(
)反応によって求めた相対測定値をTc-99の熱中性子断面積に規格化した。Tc-99試料に対する中性子自己遮蔽効果は、MCNPコードを用いた計算によって補正した。Chouらが鉛スペクトロメータを用いて測定したTc-99の中性子捕獲断面積は、本測定値より全体に高いがエネルギー依存性はよく一致している。ENDF/B-VI、JENDL-3.2の評価済核データは、5.6、20eV共鳴領域及び数100keV以上で高くなっている。本研究の後半では、鉛スペクトロメータの原理とその構築、諸特性についてまとめた。中でも、KULSの特性として(1)中性子減速時間t( s)とエネルギーE(keV)の関係(ビスマス孔:E=190/tの2乗、鉛孔:E=156/tの2乗)及び(2)エネルギー分解能(ビスマス孔、鉛孔共に約40%)に関しては共鳴フィルターを用いて実験的に求め、(3)飛行時間分析法によってKULS体系中の中性子スペクトルを測定した。一方、MCNPコードを用いてKULSの諸特性を計算した結果、全体に実験値とよい一致を示した。
s)とエネルギーE(keV)の関係(ビスマス孔:E=190/tの2乗、鉛孔:E=156/tの2乗)及び(2)エネルギー分解能(ビスマス孔、鉛孔共に約40%)に関しては共鳴フィルターを用いて実験的に求め、(3)飛行時間分析法によってKULS体系中の中性子スペクトルを測定した。一方、MCNPコードを用いてKULSの諸特性を計算した結果、全体に実験値とよい一致を示した。
米沢 仲四郎*; 松江 秀明*; 安達 武雄*; 星 三千男*
PNC TJ1500 96-001, 371 Pages, 1996/03
平成5年度及び6年度に引き続きJRR-3Mの冷中性子ビームを使用した中性子即発 線分析(PGA)により、人工バリア材料中の30Si同位体分析法の検討を行った。本年度は、1)28Si、29Si、30Siの各濃縮同位体の測定により、各同位体のPGA基礎データを求め、2)30Si拡散試験用試料調製法について、試験片を浸せき液をろ紙上に蒸発乾固する方法の検討を行い、28Si、29Si、30Si各同位体の検出限界を明らかにした。さらに、3)ケイ砂混合ベントナイト中のSiコロイドの透過を模擬したAuコロイド透過試験試料中のAuの定量を行い、Auコロイドは殆ど透過しない事を明らかにするとともに、4)海外における関連分野の研究状況を調査した。
線分析(PGA)により、人工バリア材料中の30Si同位体分析法の検討を行った。本年度は、1)28Si、29Si、30Siの各濃縮同位体の測定により、各同位体のPGA基礎データを求め、2)30Si拡散試験用試料調製法について、試験片を浸せき液をろ紙上に蒸発乾固する方法の検討を行い、28Si、29Si、30Si各同位体の検出限界を明らかにした。さらに、3)ケイ砂混合ベントナイト中のSiコロイドの透過を模擬したAuコロイド透過試験試料中のAuの定量を行い、Auコロイドは殆ど透過しない事を明らかにするとともに、4)海外における関連分野の研究状況を調査した。
*
PNC TJ1500 94-001, 30 Pages, 1994/03
JRR-3M冷中性子ビームを使用した中性子誘起即発 線分析により、人工バリア材料中の30Si分析法の検討を行った。同位体標準試料の測定により28si、30Si定量のための検量線を作成し、28si、30siの分析感度を求めた。30siトレーサー実験の分析のために、拡散試料の測定を行い、水に浸せきする試料調製法における28Si、30siの検出限界を求めた。2種類のベントナイト中の、28Si、30Siの定量を行い、その検出限界を求めるとともに、H、B、Na、Mg、Al、Si、S、Cl、K、Ca、Ti、Mn、Fe、Sm、Gdの定量を行った。元素の定量結果は、Mg、S、Mnを除き動燃の値と良い一致が得られた。
線分析により、人工バリア材料中の30Si分析法の検討を行った。同位体標準試料の測定により28si、30Si定量のための検量線を作成し、28si、30siの分析感度を求めた。30siトレーサー実験の分析のために、拡散試料の測定を行い、水に浸せきする試料調製法における28Si、30siの検出限界を求めた。2種類のベントナイト中の、28Si、30Siの定量を行い、その検出限界を求めるとともに、H、B、Na、Mg、Al、Si、S、Cl、K、Ca、Ti、Mn、Fe、Sm、Gdの定量を行った。元素の定量結果は、Mg、S、Mnを除き動燃の値と良い一致が得られた。
米澤 仲四郎; 伊藤 泰男*
Radioisotopes, 43(1), p.50 - 53, 1994/01
原子炉の中性子を利用した、中性子誘起即発 線分析(PGA)の解説を行った。PGAの原理及び特徴について記述した後、冷中性子等の低速中性子ガイドビームを中性子源としたPGAの特長について示した。更に、筆者らがJRR-3Mの冷中性子及び熱中性子ビームガイドに設置した即発
線分析(PGA)の解説を行った。PGAの原理及び特徴について記述した後、冷中性子等の低速中性子ガイドビームを中性子源としたPGAの特長について示した。更に、筆者らがJRR-3Mの冷中性子及び熱中性子ビームガイドに設置した即発 線分析装置の概要及び特性等について記述するとともに、現在JRR-3Mで行われている応用研究例の紹介も行った。最後に、PGAによる物質中の元素及び同位体の分布分析法等の、今後の発展性についても記述した。
線分析装置の概要及び特性等について記述するとともに、現在JRR-3Mで行われている応用研究例の紹介も行った。最後に、PGAによる物質中の元素及び同位体の分布分析法等の、今後の発展性についても記述した。
 線分析
線分析米澤 仲四郎
Radioisotopes, 43(11), p.727 - 728, 1994/00
冷中性子ビームを使用した即発 線研究の現状を簡単にまとめた。中性子誘起即発
線研究の現状を簡単にまとめた。中性子誘起即発 線分析(PGA)は、他の分析法では分析が困難なH、B、N、Si、P、S、Cd、Gd等の分析も可能な、多元素非破壊分析法という特長をもつ。PGAは、これまで良質な中性子源が得られないことから、分析感度が低いという欠点をもった。しかし、冷中性子ビームをPGAの中性子源とすることにより、1)反応断面積の増大、2)
線分析(PGA)は、他の分析法では分析が困難なH、B、N、Si、P、S、Cd、Gd等の分析も可能な、多元素非破壊分析法という特長をもつ。PGAは、これまで良質な中性子源が得られないことから、分析感度が低いという欠点をもった。しかし、冷中性子ビームをPGAの中性子源とすることにより、1)反応断面積の増大、2) 線バックグラウンドの大幅な低下による
線バックグラウンドの大幅な低下による 線の高検出効率測定等の利点が生じ、分析感度が改善される。このようなことから、冷中性子ビームを使用したPGAの研究が世界各地で盛んに行われている。ここでは、これまでに報告された冷中性子ビームを使用した即発
線の高検出効率測定等の利点が生じ、分析感度が改善される。このようなことから、冷中性子ビームを使用したPGAの研究が世界各地で盛んに行われている。ここでは、これまでに報告された冷中性子ビームを使用した即発 線分析装置とそれらを使用したPGAの応用研究例の紹介を行った。
線分析装置とそれらを使用したPGAの応用研究例の紹介を行った。
米澤 仲四郎; 星 三千男
JAERI-M 91-087, 44 Pages, 1991/05
原子炉の中性子を利用した即発ガンマ線分析(PGA)に関する文献を調査し、PGAの原理及び特徴を通常の中性子放射化分析(NAA)と比較しながら解説した。装置を炉内型、ビーム型及びガイドビーム型に分類し、分析化学的に使用例の多い代表的な装置を紹介するとともに、各装置の感度及び検出限界の比較を行い、その特長を利用した多方面の応用例を説明した。更に現在計画中のJRR-3(改造炉)の冷及び熱中性子ガイドビームを利用したPGAについて、設置予定の実験装置の紹介及びその研究計画を示した。
瀬川 麻里子; 前田 亮; 藤 暢輔; 甲斐 哲也
not registered
【課題】試料における中性子共鳴吸収を利用して試料の温度を非接触かつ高精度で測定する。 【解決手段】この温度測定装置1においては、白色スペクトル、パルス状の中性子線N0を発する中性子源100が用いられ、中性子線N0は、温度が測定される対象となる試料S0に照射される。試料S0を透過後の中性子線N1は、材料構成が既知であるインディケータS1に照射される。γ線検出器20によってインディケータS1から中性子線N1の照射に伴って発せられるγ線が検出される。γ線検出器20によって測定された飛行時間スペクトルには温度依存性が存在し、これを解析することによって、試料S0の温度を算出することができる。
 -ray analysis using pulsed neutrons at J-PARC
-ray analysis using pulsed neutrons at J-PARC藤 暢輔; 海老原 充*; Huang, M.; 木村 敦; 中村 詔司; 原田 秀郎
no journal, ,
Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA) is an analytical method which uses the energy of the  -rays. Elemental analysis by time of flight (TOF) uses the energy of neutron resonances. Both PGA and TOF are known as non-destructive method and use a neutron beam for sample activation and the
-rays. Elemental analysis by time of flight (TOF) uses the energy of neutron resonances. Both PGA and TOF are known as non-destructive method and use a neutron beam for sample activation and the  -rays in neutron capture reactions. However, PGA and TOF have never been applied simultaneously before. We developed a technique which combines PGA and TOF by using an intense pulsed neutron beam and a large solid angle Ge detector system. It allows us to obtain the results from both methods at the same time. PGA and TOF have different sensitivity and specificity. Therefore, the technique has considerable potential as a useful tool for non-destructive elemental analysis. Moreover, significant synergy has been achieved. Specifically, analysis of a spectrum of TOF-PGA makes it possible to quantify element concentrations in the sample that neither PGA nor TOF methods can be applied to. To assess the feasibility of the technique, we conducted experiments at the Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument (ANNRI). As a consequence, the developed technique allows us to eliminate or at least to greatly suppress the overlaps of
-rays in neutron capture reactions. However, PGA and TOF have never been applied simultaneously before. We developed a technique which combines PGA and TOF by using an intense pulsed neutron beam and a large solid angle Ge detector system. It allows us to obtain the results from both methods at the same time. PGA and TOF have different sensitivity and specificity. Therefore, the technique has considerable potential as a useful tool for non-destructive elemental analysis. Moreover, significant synergy has been achieved. Specifically, analysis of a spectrum of TOF-PGA makes it possible to quantify element concentrations in the sample that neither PGA nor TOF methods can be applied to. To assess the feasibility of the technique, we conducted experiments at the Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument (ANNRI). As a consequence, the developed technique allows us to eliminate or at least to greatly suppress the overlaps of  -rays, and provides a highly accurate determination of an elemental composition even with the presence of undesirable elements.
-rays, and provides a highly accurate determination of an elemental composition even with the presence of undesirable elements.